Introduction
Bioenergy generation does not produce emissions of greenhouse gases like fossil fuels and reduces air pollution. Having a diverse energy supply and reducing dependence on imported fuels. Moreover, resulting in the creation of economic development and jobs in the manufacturing sector.
Additionally, Bioenergy is a diverse resource that helps to meet the energy demand. Moreover, It is a renewable energy derived from organic materials like biomass used to transport fuel, heat and other products. Like wastes from home, organic farm residues and wastes are primary biomass sources.
What is Bioenergy?
Bioenergy is the energy derived from organic material to generate power. It is a renewable energy generated from biomass fuel utilization of residues, grown crops and organic waste.
Biopower converts renewable biomass fuels to heat and electricity. Moreover, Three ways to harvest energy help produce biopower burning, bacterial decay converting fuel to gas and liquid fuel.
Furthermore, Since ancient times wood, manure and charcoal have been used as a source of fire by man from the ancient days for cooking and eating in communities in developing countries. olive oils and whales are some of the bio-oil used during the 19th century.
Types of Bioenergy
- Overview of different types of bioenergy.
- Biomass energy: Moreover, This energy is derived from biomass which contains chemical energy from the sun through photosynthesis. It can be burned directly for heat or can be converted to liquid and gas processes.
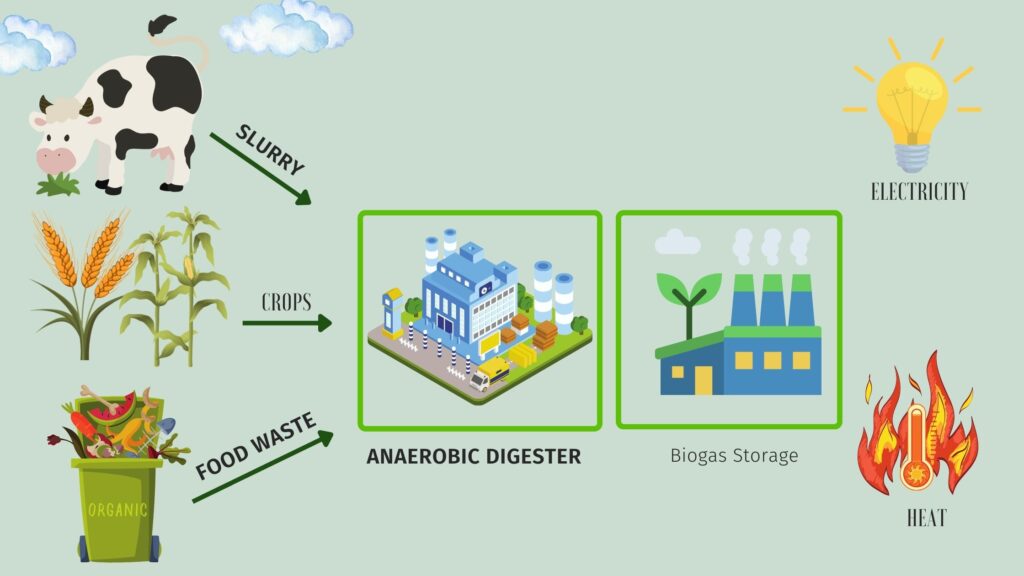
- Biogas energy: It is an environment-friendly, renewable energy produced from the breakdown of organic matter like food scraps and waste of animals.
- Biofuels: Any fuel derived from biomass were plants like algae material or waste of animals. Unlike using fossil fuels like petroleum, coal, and natural gas, feedstock materials can be replenished similar to biofuels.

Biomass and Biogas: Understanding the Difference
Furthermore, Biomass includes crops, agriculture residue, forestry residues, wood processing and municipal waste. Forest residue, purpose-grown grasses, urban wood waste, and sorted municipal waste are examples of biomass.
- How biomass energy is produced.?
Electricity is generated from direct combustion to produce higher-pressure steam. The steam flows through turbine blades causing rotations which are connected to generators producing electricity.
- Definition of biogas.
- Sources of biogas like manure, and vegetable waste. Furthermore, The composition of biogas consists of methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen and hydrogen sulfide.
- Most electricity is generated from biomass by combustion. Moreover, Biomass is burned in a boiler over a series of turbine blades causing them to rotate to produce electricity.
- Comparison between biomass and biogas.
- The primary biomass and biogas difference is biomass is a solid material whereas, biogas is a gaseous material created through the process of anaerobic digestion.
- Some pros of biogas are renewable, reliable, abundant and waste reduction. The cons are being expensive, requiring space, greenhouse and environmental impact.

Benefits of Bioenergy
- Environmental benefits.
- Reduction of greenhouse gasses: by implementing certain regulations like switching the manual or electric lawnmower, composting leftover fruit, planting your vegetables, and local products and recycling as much as possible.
- Sustainable waste management: This aims to maintain materials in use for a longer time and minimize solid waste being disposed of.
- Economic benefits.
- Job creation: this provides new jobs, for people being unemployed for finding a job.
- Energy security and independence: it refers to the availability and reliability of energy sources being energy independence to the ability to produce energy without foreign sources.
- Social benefits.
- Health improvements: enjoying de-stressing, putting away salt, going to bed earlier, checking posture, doing a crossword puzzle and making a dietary substitution.
- Rural development: Moreover, by providing energy at the local level, bioenergy makes a significant contribution to social and economic development in areas like rural areas.

Challenges and Future of Bioenergy
- Current challenges in bioenergy adoption.
- Technological limitations: non-food-based biomass primarily relies on supplies from agricultural residue and waste. However, resources are insufficient to allow bioenergy and biofuel plays a major role in the renewable and alternative energy market.
- Economic and policy barriers: due to higher initial costs, lack of proper financial assistance delays the financial dimension of policy. Moreover, Barriers like inadequate government policies, parameters and short-term contracts.
- Prospects and innovations.
- Advances in bioenergy technology: Moreover, lignocellulosic feedstock such as forestry residue, industrial waste, and other residue streams produce bioenergy with low CO2 emissions and high greenhouse gas reduction.
- Potential policy changes and incentives: Moreover, 40 lakhs or a maximum of 5 crores per project are some of the incentives provided for bioenergy. Some of the impacts include competition for land, emissions for land use, deforestation and biodiversity loss.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Bioenergy enables the reuse of carbon from the waste streams like emissions from fuels for cars, trucks, jets and ships. Bioproducts are renewable power. To know more about bioenergy visit cryptogreen force.
Moreover, avoiding new investments in conventional sectors with increased bioenergy resources would help India reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels. Furthermore, Biomass represents the equivalent amount of carbon absorbed with near-zero emissions.
Bioenergy is the largest source of renewable energy globally by 6%. Researchers estimate by 2030 bioenergy is set to replace fossil fuels.

FAQ Section
- How is bioenergy produced?
You use plant and organic matter to generate electricity called bioenergy. Bioenergy is a renewable energy from organic matters like harvest, residue, purpose-grown crops and so on.
- What is the difference between biomass and biogas?
The primary difference between biomass and biogas is biomass is solid whereas biogas is gaseous. However, both are created in the process of anaerobic digestion.
- What are the advantages of bioenergy?
Moreover, Some advantages of bioenergy are providing energy security, reducing greenhouse emissions, supporting the agriculture industry and providing new jobs.
- What are the challenges facing bioenergy?
Moreover, the development of feedstock includes non-biomass feedstock that relies on supplies from the agriculture sector. Furthermore, These resources allow bioenergy and biofuel to play a role in renewable and alternative energy.
- What is the future of bioenergy?
Furthermore, Researchers estimate the future of biogas is around 55% of renewable energy. The result of emission is estimated at 6%. Around 2030 bioenergy is set to replace fossil fuels.


